Check Best Thermostat Pricing in Amazon
** As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.
A coolant thermostat regulates engine temperature by controlling coolant flow to the radiator. It opens and closes based on temperature.
A coolant thermostat plays a crucial role in an engine’s cooling system. It ensures the engine operates within an optimal temperature range. This small device opens to allow coolant flow to the radiator when the engine heats up. It closes when the engine cools down to maintain the ideal temperature.
This process helps prevent engine overheating and ensures efficient performance. Proper thermostat function is vital for engine longevity and fuel efficiency. Regular maintenance and checks can ensure the thermostat works correctly, avoiding potential engine issues. Understanding its role can help in diagnosing cooling system problems effectively.

Credit: www.birdman308.com
- Introduction To Coolant Thermostats
- Basic Functionality Of Coolant Thermostats
- Types Of Coolant Thermostats
- Installation And Placement
- Temperature Regulation Mechanics
- Symptoms Of Thermostat Failure
- Maintaining And Replacing A Coolant Thermostat
- Advancements In Thermostat Technology
- The Environmental Impact Of Proper Thermostat Operation
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
Introduction To Coolant Thermostats
A coolant thermostat is a small yet crucial component in an engine. It helps regulate the engine’s temperature. Without it, engines could overheat or run too cold. This blog post explores how a coolant thermostat works.
Purpose In Engine Temperature Regulation
The main job of a coolant thermostat is to manage the engine’s temperature. It keeps the engine from getting too hot or too cold. A well-regulated engine performs better and lasts longer.
When the engine is cold, the thermostat stays closed. This helps the engine warm up quickly. Once the engine reaches a certain temperature, the thermostat opens. This allows coolant to flow through the engine. The coolant absorbs excess heat and prevents overheating.
Temperature control is vital for engine health. It ensures that all parts function optimally. Engines that run too hot can suffer damage. Engines that run too cold waste fuel and emit more pollutants.
Brief History Of Thermostat Development
The development of thermostats dates back to the early 20th century. Early engines lacked effective temperature control. This led to frequent overheating and engine damage.
Inventors soon realized the need for better temperature regulation. The first thermostats were simple mechanical devices. They used wax or metal components that expanded and contracted with temperature changes.
Over time, thermostat technology evolved. Modern thermostats are more reliable and efficient. They use advanced materials and precise engineering. This ensures better temperature control and longer engine life.
| Year | Development |
|---|---|
| Early 1900s | First mechanical thermostats introduced |
| Mid-1900s | Improved materials and designs |
| Late 1900s to Present | Advanced thermostats with better precision |
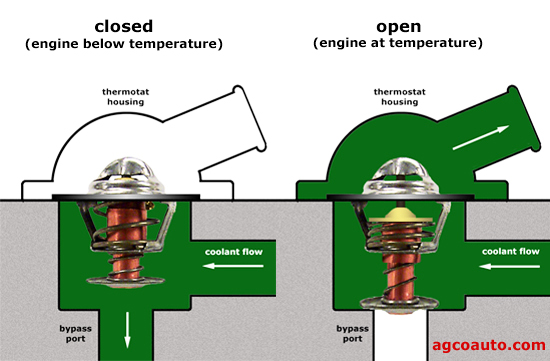
Credit: www.agcoauto.com
Basic Functionality Of Coolant Thermostats
The coolant thermostat plays a crucial role in a vehicle’s engine. It helps regulate the engine’s temperature by controlling coolant flow. Understanding its basic functionality can help you maintain your vehicle better.
The Role Of Wax Pellets
Inside the thermostat, there are wax pellets. These pellets are sensitive to temperature changes. As the engine heats up, the wax melts and expands.
The expansion of the wax pushes a piston. This piston movement helps in opening the valve. Once the valve opens, coolant can flow through the engine.
Valve Operation And Flow Control
The valve in the thermostat opens and closes to control the coolant flow. When the engine is cold, the valve stays closed. This prevents coolant from flowing, allowing the engine to warm up quickly.
As the engine reaches the optimal temperature, the wax expands. The valve then opens to let coolant flow through the engine. This helps maintain a stable temperature.
| Engine Temperature | Thermostat Action |
|---|---|
| Cold | Valve Closed |
| Optimal | Valve Opens |
| Overheating | Valve Fully Open |
Maintaining the right engine temperature is crucial. The thermostat ensures your engine runs efficiently and avoids overheating.
Types Of Coolant Thermostats
Coolant thermostats are essential for vehicle engines. They regulate the engine’s temperature. There are two main types of coolant thermostats. Each type works differently to maintain optimal engine performance.
Traditional Bimetallic Strip Designs
Traditional coolant thermostats use a bimetallic strip. This strip is made of two different metals. These metals expand at different rates when heated. The bimetallic strip bends as the temperature changes.
When the engine is cold, the thermostat remains closed. It prevents coolant from flowing. As the engine warms up, the bimetallic strip bends. This bending action opens the valve. Coolant then flows through the engine. This process helps regulate the engine’s temperature.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Bimetallic Strip | Bends with temperature changes |
| Valve | Opens and closes to regulate coolant flow |
Modern Electronic Thermostats
Modern electronic thermostats use sensors and electronic control units (ECUs). These components provide more precise temperature control. Sensors monitor the engine’s temperature continuously.
The ECU processes the sensor data. It then sends signals to open or close the thermostat valve. This system allows for more accurate temperature regulation. It also improves fuel efficiency and reduces emissions.
- Sensors: Monitor engine temperature
- ECU: Processes data and controls the valve
Modern electronic thermostats are more reliable. They adjust quickly to temperature changes. This ensures the engine operates efficiently under various conditions.
Installation And Placement
Installation and Placement of a coolant thermostat play a crucial role in engine performance. Correct installation ensures optimal temperature control. Proper placement within the cooling system helps maintain engine efficiency and longevity.
Common Locations In The Cooling System
The thermostat is typically located near the engine block. It can also be found at the coolant outlet. In some vehicles, it’s placed in a housing connected to the upper radiator hose.
| Location | Description |
|---|---|
| Near Engine Block | Helps regulate engine temperature quickly. |
| Coolant Outlet | Controls the flow of coolant to the radiator. |
| Upper Radiator Hose | Ensures efficient heat exchange. |
Impact On Engine Performance
A properly installed thermostat ensures the engine warms up quickly. It also prevents overheating by regulating coolant flow. This helps maintain fuel efficiency and reduces wear and tear on engine components.
- Quick Warm-Up: Reduces fuel consumption.
- Prevents Overheating: Protects engine parts from damage.
- Maintains Efficiency: Keeps engine running smoothly.
Temperature Regulation Mechanics
The temperature regulation mechanics of a coolant thermostat are crucial for engine efficiency. These mechanics control the engine’s operating temperature. This helps in maintaining optimal performance and preventing overheating.
Thermostat Opening And Closing Temperatures
The coolant thermostat opens and closes at specific temperatures. When the engine starts cold, the thermostat remains closed. This allows the engine to warm up quickly. Once the engine reaches a certain temperature, the thermostat opens. This lets coolant flow and regulates the temperature.
Most thermostats open between 180-195 degrees Fahrenheit. This range ensures the engine runs at its most efficient temperature. If the temperature drops, the thermostat closes again. This helps maintain the optimal temperature range.
Effects On Engine Warm-up
A properly functioning thermostat shortens the engine warm-up time. This is important for reducing engine wear. A quick warm-up means less fuel is used. This improves fuel efficiency.
If the thermostat sticks open, the engine takes longer to warm up. This can lead to increased fuel consumption and engine wear. Conversely, if the thermostat sticks closed, the engine can overheat. This can cause severe engine damage.
Check Best Thermostat Pricing in Amazon
** As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.
The table below summarizes the effects of thermostat behavior on engine performance:
| Thermostat Behavior | Effect on Engine |
|---|---|
| Sticks Open | Longer warm-up, increased fuel use |
| Sticks Closed | Overheating, potential engine damage |
| Proper Operation | Optimal temperature, efficient performance |

Credit: www.certifiedautoca.com
Symptoms Of Thermostat Failure
Understanding the symptoms of a failing coolant thermostat can help prevent severe engine damage. A malfunctioning thermostat can cause various issues that affect engine performance. Below are some common symptoms and diagnostic tips.
Overheating And Underheating Issues
Overheating is a clear sign of thermostat failure. When the thermostat is stuck closed, coolant cannot flow to the radiator. This causes the engine to overheat quickly.
On the other hand, underheating can occur if the thermostat is stuck open. This prevents the engine from reaching its optimal operating temperature. A cold engine may perform poorly and consume more fuel.
Look for these signs to identify overheating and underheating issues:
- Temperature gauge readings are too high or too low.
- Engine takes too long to warm up or overheats quickly.
- Poor heater performance inside the car.
Diagnostic Tips
Use these diagnostic tips to determine if your thermostat is failing:
- Check the temperature gauge: Observe the gauge after starting the engine. If it rises quickly or stays low, the thermostat may be faulty.
- Feel the radiator hoses: Carefully touch the upper and lower radiator hoses. If one is hot and the other is cold, the thermostat might be stuck.
- Listen for unusual sounds: A stuck thermostat can cause unusual noises from the engine area. Listen for gurgling or bubbling sounds.
By following these tips, you can diagnose thermostat issues early and prevent engine damage.
Maintaining And Replacing A Coolant Thermostat
The coolant thermostat is a vital part of your vehicle’s cooling system. It helps regulate the engine’s temperature. Proper maintenance and timely replacement ensure optimal performance. This section covers everything you need to know about maintaining and replacing a coolant thermostat.
Recommended Service Intervals
Regular maintenance of your coolant thermostat is crucial. Most experts recommend replacing the thermostat every 50,000 to 100,000 miles. This helps prevent overheating and ensures your engine runs smoothly. Always check your vehicle’s manual for specific intervals.
Step-by-step Replacement Guide
Replacing a coolant thermostat involves a few essential steps. Follow this guide to ensure a smooth process:
- Cool Down the Engine: Make sure the engine is completely cool before you start.
- Drain the Coolant: Place a drain pan under the radiator and open the drain valve.
- Remove the Hose: Disconnect the hose attached to the thermostat housing.
- Take Out the Thermostat: Remove the bolts and take out the old thermostat.
- Clean the Surface: Clean the housing surface to ensure a proper seal.
- Install the New Thermostat: Place the new thermostat in the housing and secure it with bolts.
- Reconnect the Hose: Attach the hose back to the thermostat housing.
- Refill the Coolant: Fill the radiator with coolant and ensure there are no leaks.
- Start the Engine: Start the engine and check for any leaks or issues.
By following these steps, you can replace your coolant thermostat efficiently.
Advancements In Thermostat Technology
Understanding how a coolant thermostat works has evolved over the years. Early designs were simple, but technology has made them smarter and more efficient. These advancements improve engine performance and enhance temperature management.
Smart Thermostats And Engine Efficiency
Smart thermostats are a big leap in engine technology. They use sensors to monitor and adjust the engine’s temperature in real-time. This ensures the engine runs at its optimal temperature, reducing wear and tear.
Benefits of Smart Thermostats:
- Improved fuel efficiency
- Reduced emissions
- Longer engine life
Smart thermostats also provide data to the car’s computer. This data helps in diagnosing problems early. It makes maintenance easier and more effective.
Future Trends In Temperature Management
Future trends point towards even more advanced temperature management systems. These systems will be integrated with AI to predict and adjust temperatures. They will consider various factors such as weather, driving conditions, and engine load.
Potential Future Features:
- AI-driven temperature control
- Self-adjusting thermostats
- Enhanced diagnostic capabilities
These advancements will make engines more efficient and eco-friendly. They will also reduce the need for frequent maintenance, saving time and money for vehicle owners.
The Environmental Impact Of Proper Thermostat Operation
The coolant thermostat plays a crucial role in your vehicle. It ensures the engine operates at the right temperature. This not only enhances performance but also has significant environmental benefits.
Reducing Emissions Through Optimal Temperature
An optimally functioning thermostat helps the engine reach its ideal temperature quickly. This reduces harmful emissions. A cold engine produces more pollutants. A properly working thermostat minimizes this by maintaining a steady, optimal temperature.
Carbon monoxide and hydrocarbons are two major pollutants. They are higher during the engine’s warm-up period. An efficient thermostat reduces this period, thus lowering emissions. This contributes to a cleaner environment.
Fuel Efficiency And Thermostat Health
An efficient thermostat improves fuel efficiency. The engine runs more efficiently at its optimal temperature. This means less fuel consumption. Lower fuel consumption means fewer emissions.
A faulty thermostat can lead to overheating or overcooling. Both conditions reduce fuel efficiency. Regular maintenance ensures your thermostat is in good health. This promotes better fuel economy and a greener environment.
| Condition | Impact on Environment |
|---|---|
| Optimal Temperature | Reduced emissions, better fuel efficiency |
| Overheating | Increased emissions, lower fuel efficiency |
| Overcooling | Increased emissions, lower fuel efficiency |
Regular checks and maintenance of the thermostat are essential. It ensures the engine runs at the right temperature. This promotes a healthier environment and better vehicle performance.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Do I Know If My Coolant Thermostat Is Bad?
Your coolant thermostat may be bad if your engine overheats or runs unusually cold. Check for fluctuating temperature gauge readings. Reduced heater performance and coolant leaks can also indicate a faulty thermostat.
How Does A Car Coolant Thermostat Work?
A car coolant thermostat regulates engine temperature. It stays closed when the engine is cold, allowing it to warm up. Once the engine reaches optimal temperature, the thermostat opens, letting coolant flow to prevent overheating. This ensures efficient engine performance.
How Do Thermostats Open And Close?
Thermostats open and close based on temperature changes. They use sensors to detect temperature and activate switches. This process regulates heating and cooling systems efficiently.
Can You Drive With A Bad Coolant Thermostat?
Driving with a bad coolant thermostat is risky. It can cause engine overheating or underheating. Replace it immediately to avoid damage.
Conclusion
Understanding how a coolant thermostat works is essential for vehicle maintenance. It regulates engine temperature, ensuring optimal performance. Regular checks can prevent overheating and costly repairs. Maintaining your thermostat contributes to a smooth-running engine, extending your car’s lifespan. Stay informed and keep your vehicle in top shape.
Check Best Thermostat Pricing in Amazon
** As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.


